Towards superior retinal biomarkers
Novel retinal imaging biomarkers in various retinal and ocular conditions, as well as cardiovascular risk factors and systemic diseases, are being investigated using the rtx1 Adaptive Optics Retinal Camera.
Over 300 peer-reviewed publications have reported clinically relevant cellular and microvascular alterations – including qualitative and quantitative assessments – that provided novel insight such has cellular-level phenotyping, and short-term information on disease progression and therapy effects.
See below a selection of highlighted publications.

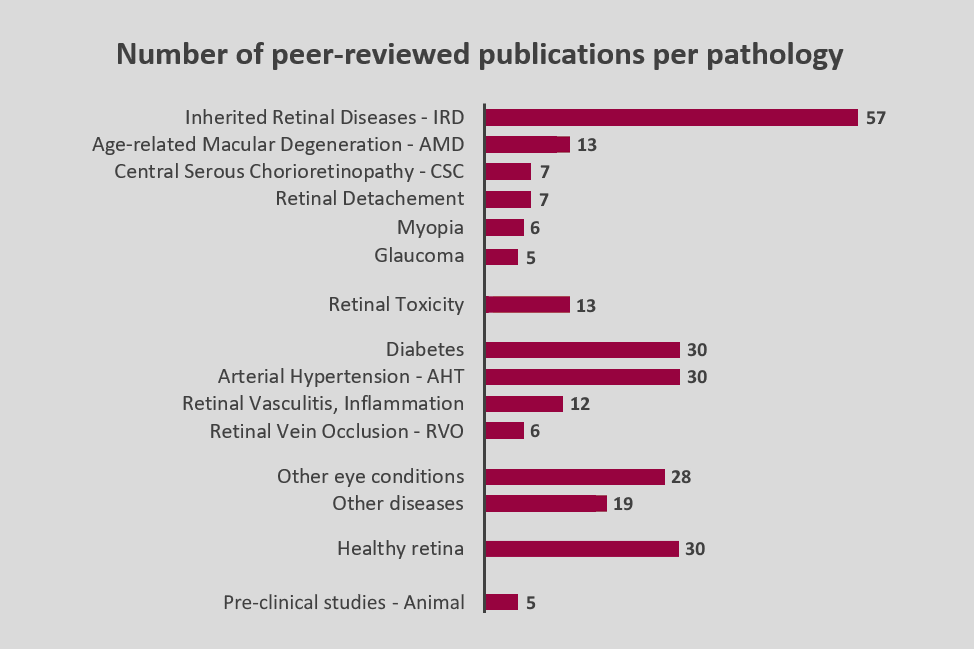
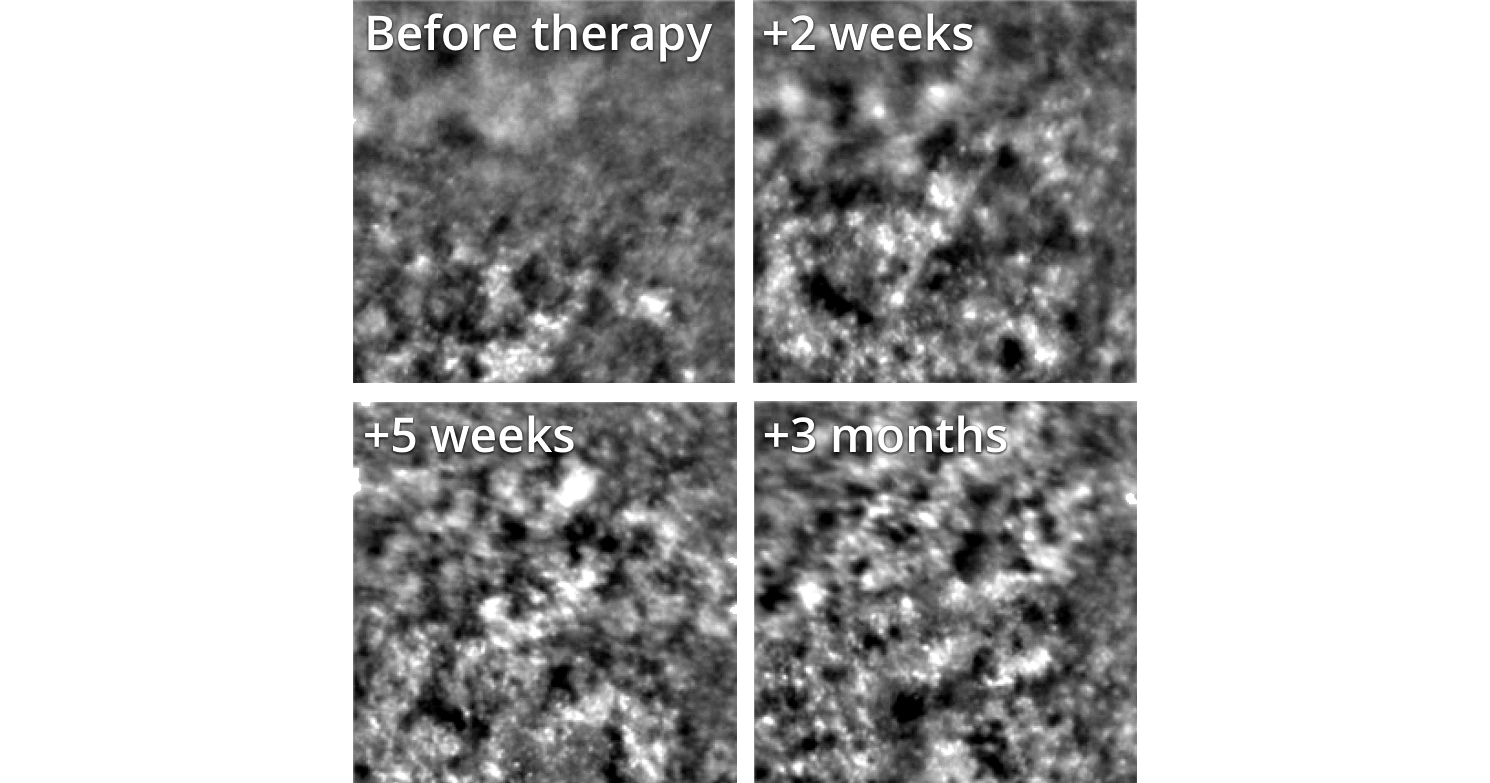
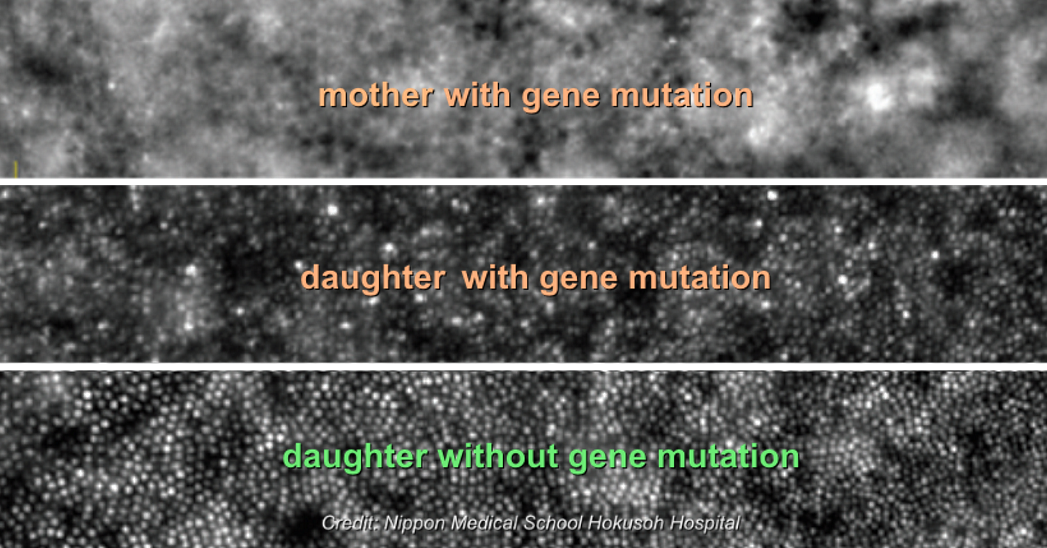

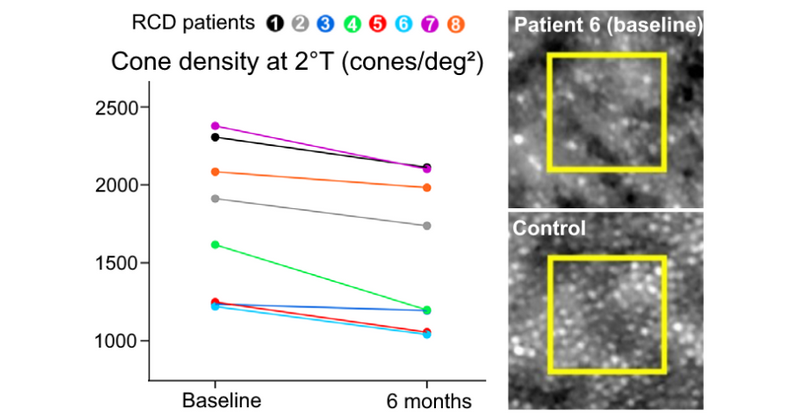
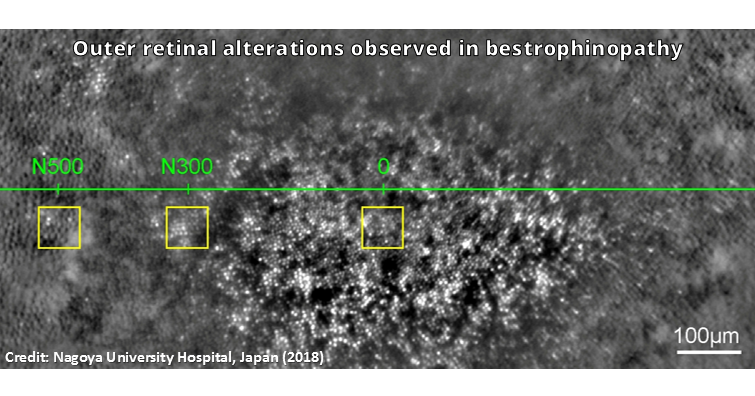
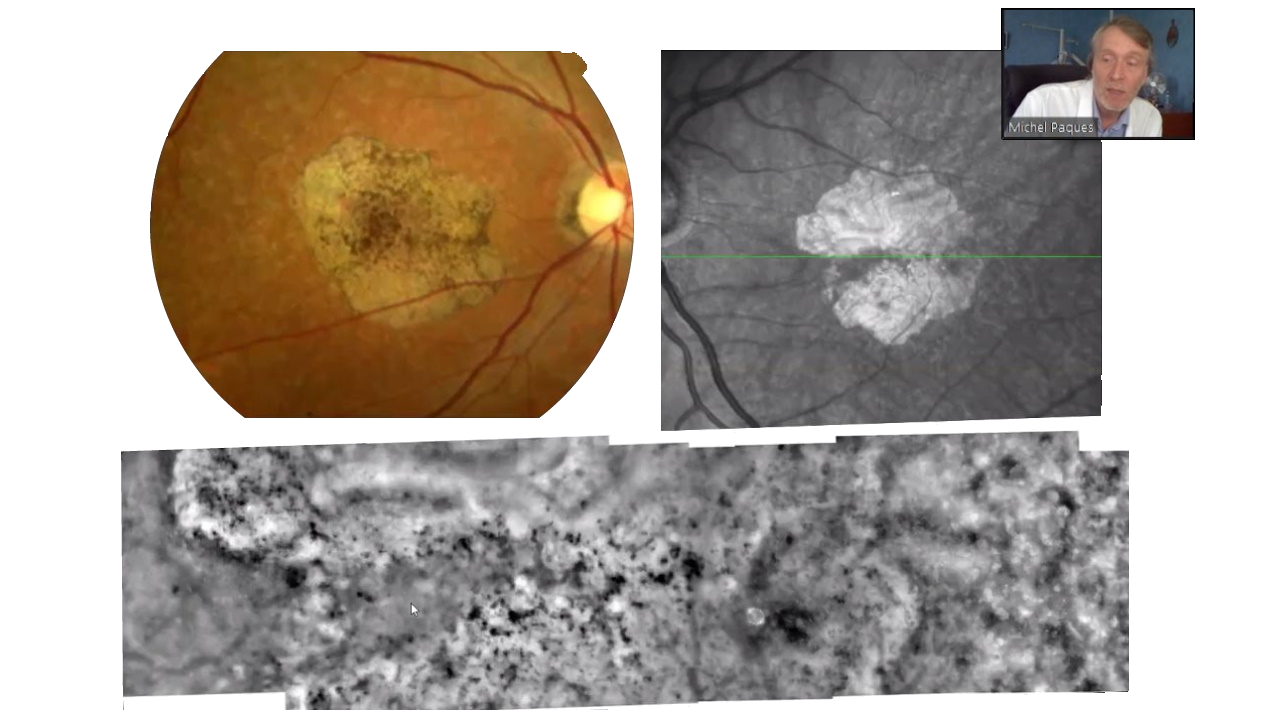
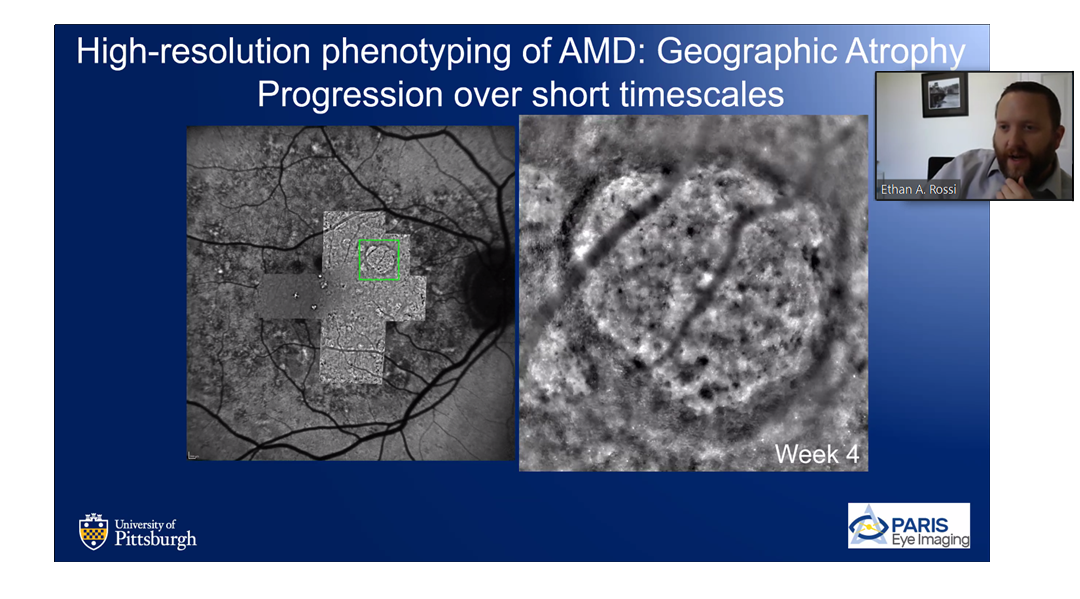
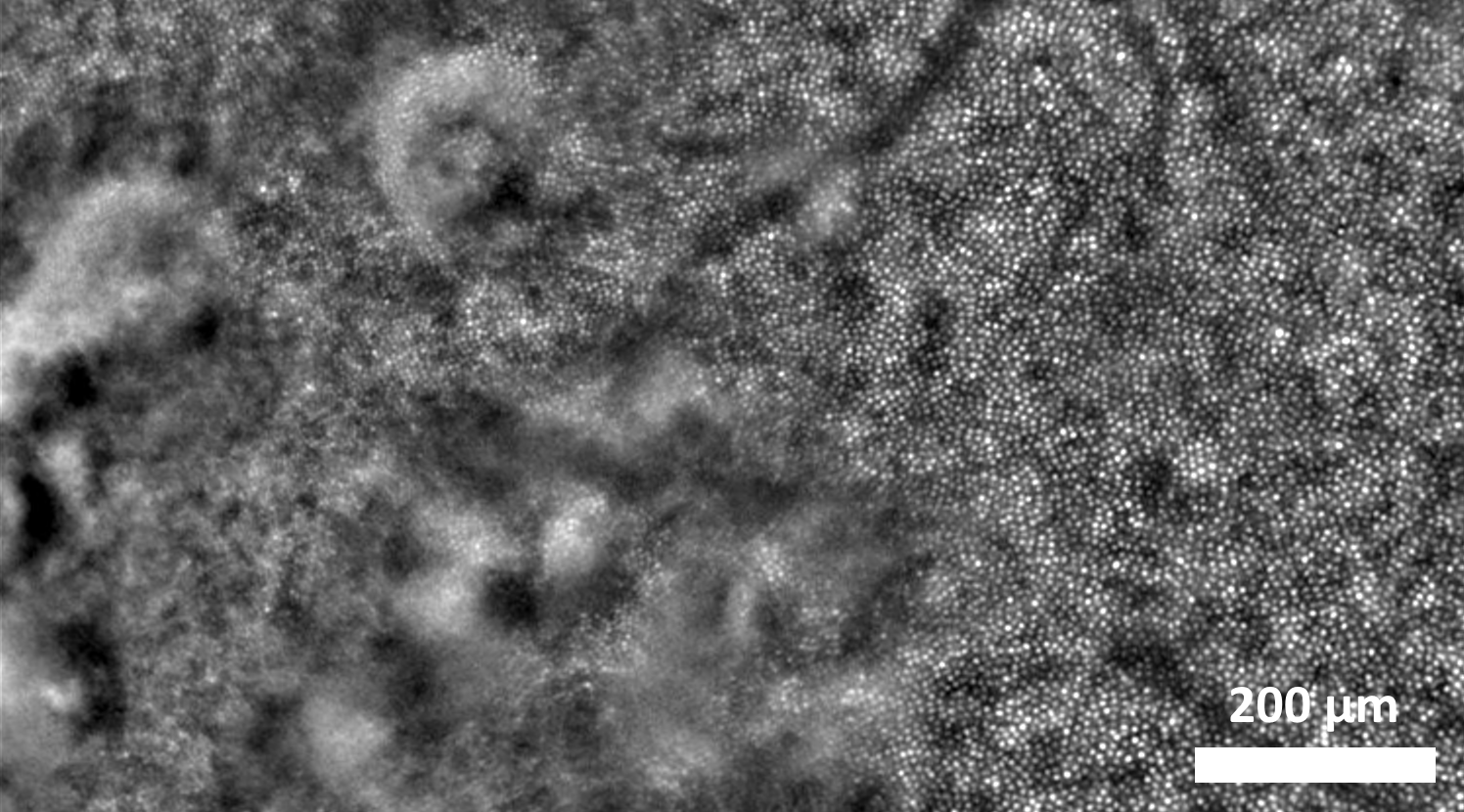
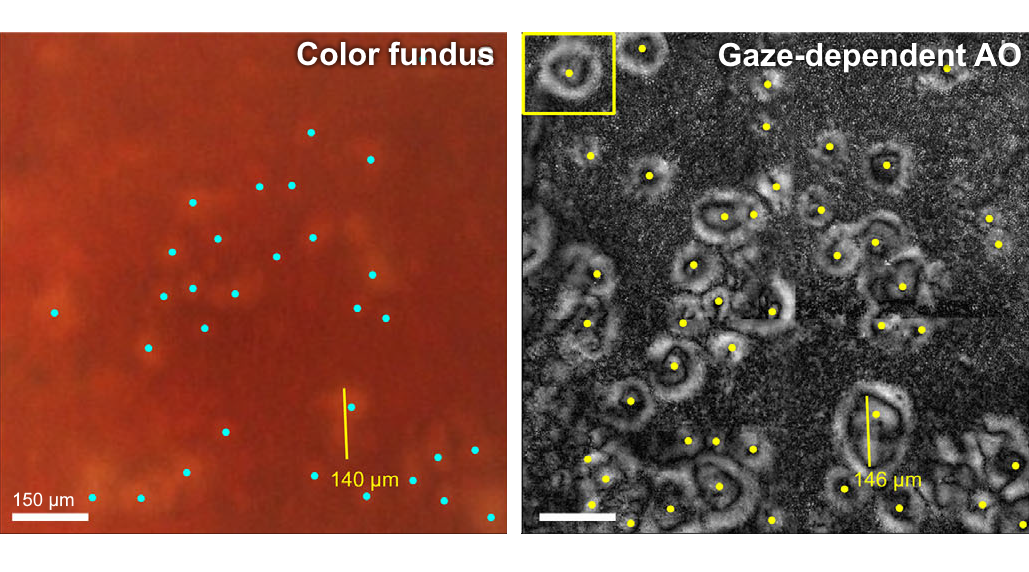
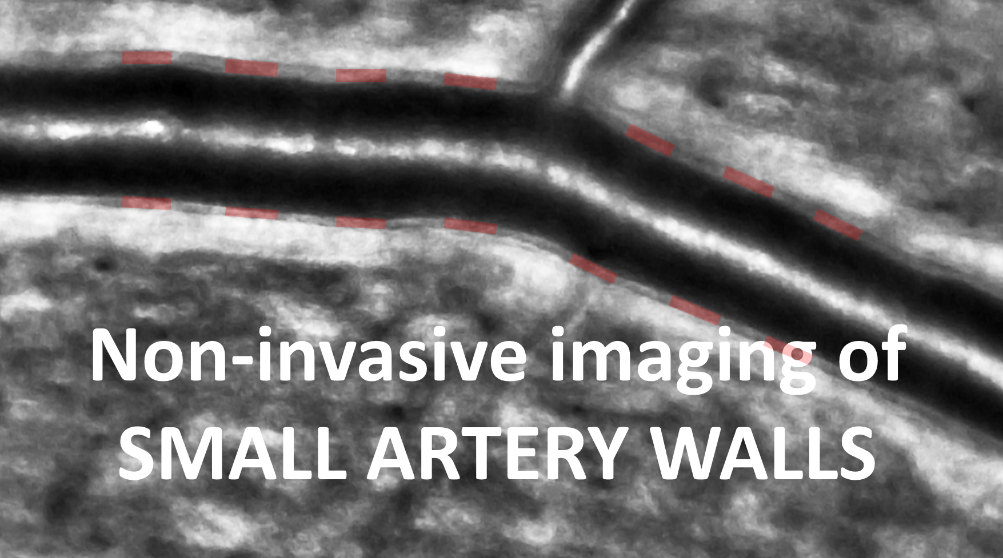
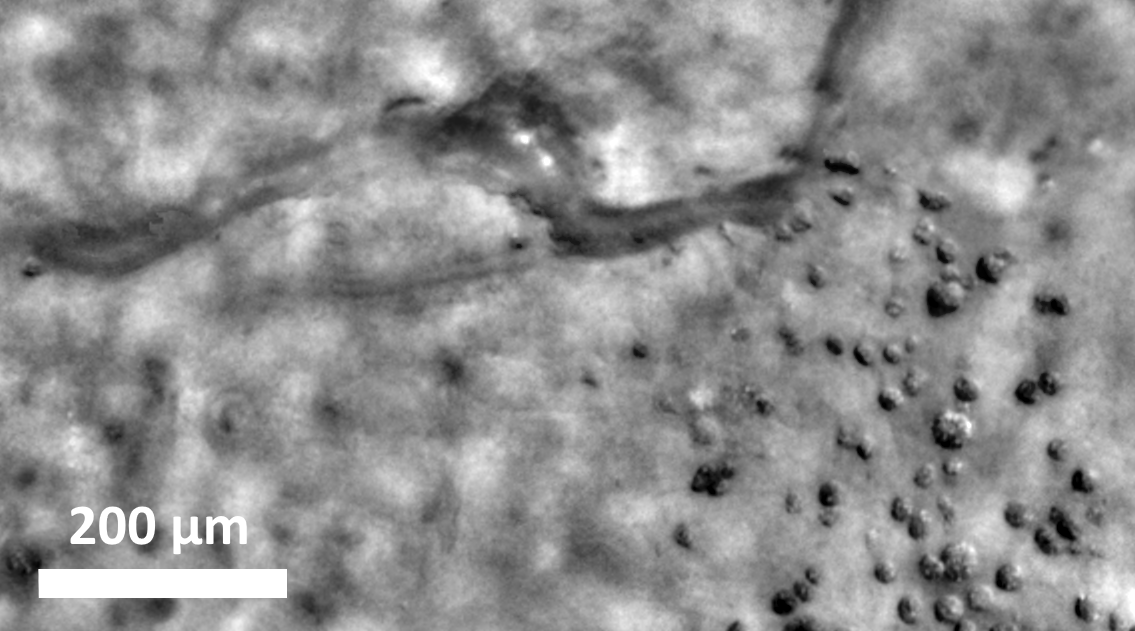
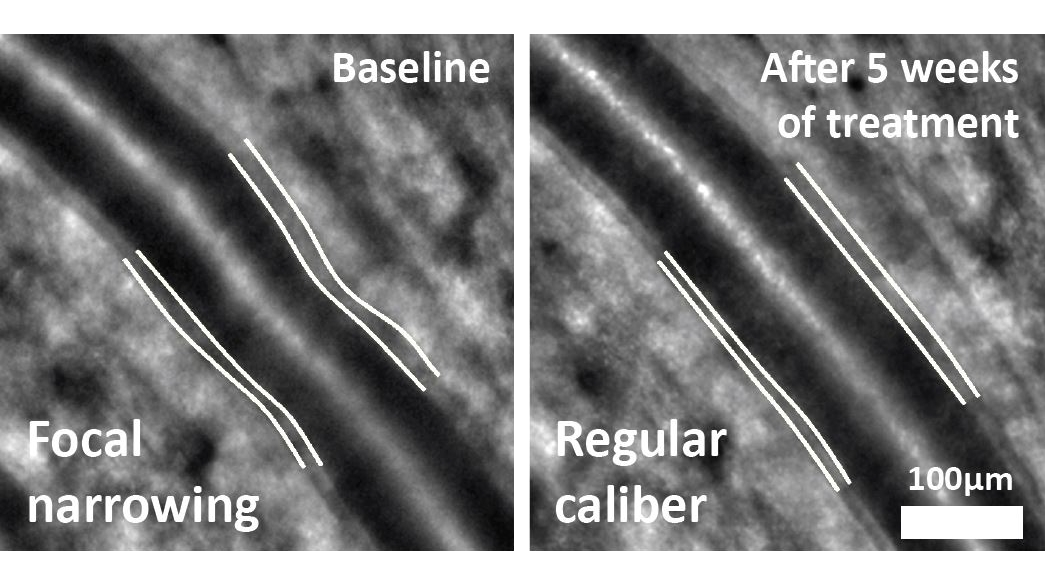
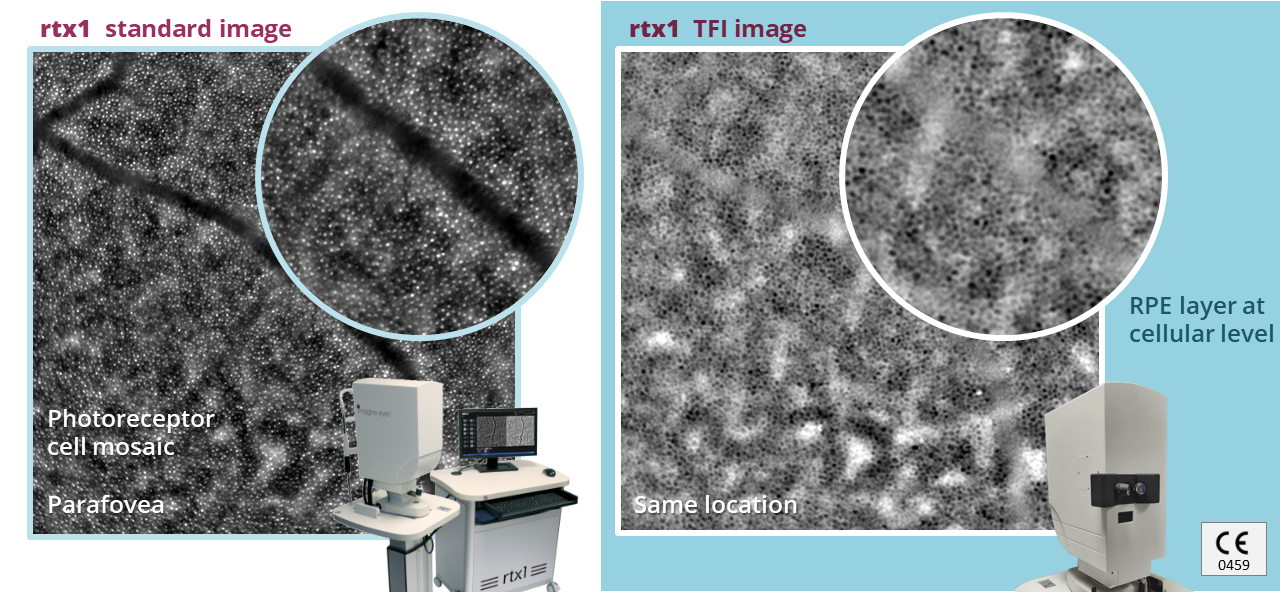
Regenerative retinal therapy evaluated with adaptive optics imaging
Sensitive assessment of retinal structure and function in Usher syndrome
Photoreceptor cells quantified in RP with and without CME
Visual cell loss revealed in asymptomatic RPGR mutation carriers
Adaptive optics reveals undetected microcysts in retinal neurodegeneration